Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD19 Monoclonal Antibody (LE-CD19)

Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Marca: Invitrogen™ MA181724
Descrizione
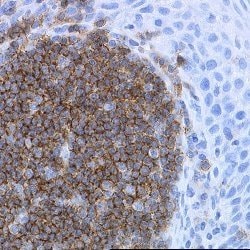
Membrane permeabilization is required for flow cytometry applications. For FACS analysis, use 10 μL of the suggested working dilution to label 1x10^6 cells in 100 μL. A suggested positive control for immunohistochemical applications is tonsil. Mouse anti Human CD19 antibody, clone LE-CD19 recognizes an epitope within the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail sequence of human CD19, a single pass type I transmembrane glycoprotein containing two C2 type Ig-like domains in the N-terminal extracellular region and four potential phosphorylation sites for tyrosine together with a single serine in the cytoplasmic region.
CD19 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, characterized by two Ig-like domains, and is expressed on B cells throughout all stages of development, excluding terminally differentiated plasma cells. It is also expressed on follicular dendritic cells and has been observed on myeloid leukemia cells, particularly those of monocytic lineage. CD19 is considered the earliest and broadest B cell-restricted antigen, and its expression is found in all B cell precursor leukemias. CD19 forms a multimolecular complex with CD21, CD81, Leu13, MHC class II, and the B cell receptor (BCR), playing a crucial role in B cell signaling. As a signal-amplifying coreceptor for the BCR, CD19 lowers the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation, allowing B cells to respond specifically and sensitively to various antigens through low-affinity antigen receptors. Signaling through CD19 induces tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium flux, and proliferation of B cells. Beyond its role as a BCR coreceptor, CD19 can also signal independently of BCR co-ligation, serving as a central regulatory component upon which multiple signaling pathways converge. This makes CD19 an important functional regulator of both normal and malignant B cell proliferation. Mutations in the CD19 gene can result in hypogammaglobulinemia, a condition characterized by low levels of immunoglobulins, while CD19 overexpression can lead to B cell hyperactivity. CD19 is expressed on 100% of peripheral B cells, as defined by the expression of kappa or lambda light chains, underscoring its significance in B cell function and immune regulation.
Specifica
| CD19 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| P15391 | |
| Cd19 | |
| CD19 peptide CGPDPAWGGGGRMGTWSTR (C-Terminus) coupled to KLH (aa 539-556). | |
| 20 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 |
| ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | |
| LE-CD19 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Cd19 | |
| AW495831; B4; B-lymphocyte antigen CD19; B-lymphocyte surface antigen B4; Cd19; CD19 antigen; CD19 molecule; CVID3; differentiation antigen CD19; Leu-12; T-cell surface antigen Leu-12 | |
| Mouse | |
| Protein A | |
| RUO | |
| 930 | |
| Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles. | |
| Liquid |
Fornite il vostro feedback sul contenuto del prodotto compilando il modulo sottostante.